Having trouble losing weight? Inflammation, not fat, might be the issue. Learn how an anti-inflammatory diet can help you reduce weight and improve health.
Ever wonder why doctors, dietitians, and health experts worldwide praise the anti-inflammatory diet? It is not just about maintaining a healthy weight, it is also a key to better overall health.
Inflammation itself is not always harmful. When you get a cut or catch a cold, your body uses inflammation to heal. But chronic inflammation is a different story. Triggered by unhealthy eating habits and certain lifestyle choices, it acts like a slow-burning fire inside your body and increases the risk of heart disease, arthritis, Alzheimer’s, and more.
Adopting this diet could transform your life and help you feel better, live longer, and stay healthier. Ready to know how? Let’s dive in.
What is an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
Some foods can trigger or worsen inflammation, while others, like anti-inflammatory foods, can help fight it. These foods contain beneficial compounds like antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and fibre that work to protect your body.
Antioxidants, found in fresh fruits and vegetables, are essential to this diet. They help neutralise free radicals (unstable molecules produced during metabolism) and prevent cell damage.
Omega-3 fatty acids, present in foods like walnuts and flaxseeds, are also known to lower inflammatory proteins in the body. Similarly, fibre-rich foods, like lentils and whole grains, significantly reduce inflammation through diet.
Why is it Important?
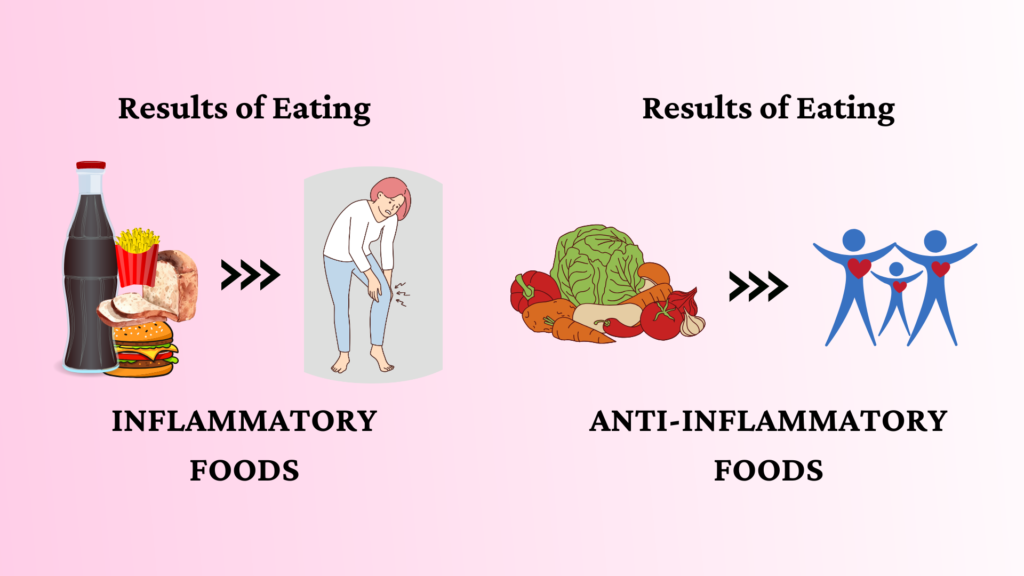
Chronic inflammation is a silent contributor to many health issues, like:
- Arthritis: Inflammation is a primary factor in joint pain and stiffness. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce these symptoms and improve joint function.
- Diabetes: Chronic inflammation can interfere with insulin function and increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. This diet helps manage blood sugar levels and reduce this risk.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Inflammation contributes to the development of heart diseases by promoting the buildup of arterial plaque. Adopting this diet lowers this risk and supports heart health.
- Weight Management: Inflammation disrupts metabolism, making weight loss more challenging. This diet supports metabolic processes and helps in weight management.
Beyond disease prevention, reducing inflammation through diet offers additional benefits:
- Improved Energy: A diet rich in non-inflammatory foods can improve overall vitality and reduce fatigue.
- Better Digestion: This diet supports a healthy gut, thereby improving digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Long-Term Health: Consistently consuming non-inflammatory foods can contribute to overall well-being and longevity.
Foods That Reduce Inflammation

A well-rounded anti-inflammatory diet includes various foods that reduce inflammation. These foods offer both nutrients and antioxidants to support overall health. Focus on vegetables like kale, spinach, broccoli, and fruits like blueberries, blackberries, strawberries, and cherries for vitamins and minerals.
Other anti-inflammatory foods include beans, nuts, seeds, and olives, along with fibre-rich whole grains. Spices like ginger and turmeric, known for their anti-inflammatory properties, are also great additions to your meals.
Do not forget about anti-inflammatory drinks like green tea, which is packed with antioxidants, or probiotic-rich beverages like kombucha. Incorporating a mix of these foods and drinks into your diet can help reduce inflammation, promote healing, and improve overall health.
Inflammatory Foods to Avoid

While following an anti-inflammatory diet, it is essential to limit some inflammatory foods to avoid triggering adverse effects in your body. Processed foods, like chips, crackers, and premade desserts like cookies or ice cream, often contain added sugar, unhealthy oils, and excess salt, which can worsen inflammation. Refined carbs, like those in white bread, pasta, and baked goods, should also be minimised.
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to chronic inflammation and should be kept in check. Moreover, some individuals may experience inflammation due to food intolerances, including gluten, dairy, or specific vegetables like nightshades (tomatoes, eggplants) or cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, cabbage).
When you recognise these triggers and focus on wholesome alternatives, you can manage inflammation effectively and support better health while reducing discomfort and related health risks.
Key Takeaway
An anti-inflammatory diet can play a crucial role in reducing inflammation and managing symptoms of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. While there’s no one-size-fits-all approach, focusing on fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can make a significant difference. These nutrient-packed foods help combat chronic inflammation, promoting better overall health and energy levels.
For those dealing with inflammation-related health issues, consulting a healthcare professional for personalized dietary guidance is essential. Embracing an anti-inflammatory lifestyle isn’t just about addressing health concerns—it’s a step toward feeling better and living a healthier, more vibrant life.
Read more